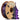3d printing resin is a liquid that hardens when hit by ultraviolet light. People use this material with resin printers like sla printers, DLP, or LCD/MSLA models. These printers make 3d objects with lots of detail. Resin printing is special because it makes smooth surfaces. It also shows tiny details in 3d models. Many people pick resin 3d printing instead of Filament. This is because it makes parts with sharp edges and tricky shapes. The sla process is still very popular. Sla printers make up a $1.6 billion market.
More people are using resin printing now. This is true for jobs that need very exact parts. Eryone and other brands have first resin printer choices for beginners.
Key Takeaways
- 3D printing resin is a liquid. It hardens when UV light shines on it. This makes smooth and detailed 3D objects.
- There are different resin types for special uses. Some are tough, some bend, and some resist heat.
- Resin printers make models one layer at a time. They use UV light for this. This gives very exact shapes and tiny details.
- Resin printing makes smoother and sharper objects than filament printing. But it costs more. You also need to be careful and follow safety rules.
- People use resin printing for miniatures, dental models, and jewelry. It is also used for strong engineering parts. This is because it is very accurate and looks nice.
What Is 3D Printing Resin
Definition
3d printing resin is a liquid photopolymer. People use it in sla printers, DLP, and LCD machines. This resin turns solid when it gets ultraviolet light. The process is called curing. The printer shines UV light on the resin to make each layer. The light makes the resin harden. Sla printers use this to make objects with smooth surfaces and fine details. The printer cures each layer until the model is finished. Curing resin one layer at a time gives high precision.
Types of Resin
There are many kinds of resins for 3d printing. Each kind has its own job. The main types are:
- Standard resin: Used for most 3d prints. It gives good detail and smooth looks.
- Engineering resin: Made to be strong and last long. It is good for working parts.
- Functional resin: Used for special needs, like flexible or tough parts.
- Ceramic resin: Has ceramic bits inside. It can take high heat after firing.
- Tough resin: Does not break or bend easily. It is good for parts that need to handle force.
- Elastomeric resin: Bends and stretches well. It is used for soft, rubbery parts.
- High-temperature resin: Handles heat. It is used where things get hot.
Note: Each resin type is made for a certain use. For example, tough resin is best for parts that bend but do not break. High-temperature resin is for places with lots of heat.
How well 3d printing resin works can change with its mix and curing temperature. For example, a study tested a new resin called polybutadiene polyurethane acrylate. When mixed 65:35 and cured at -25 °C, it had a tensile strength of 32.9 MPa and could stretch 246.1%. These numbers were much higher than at room temperature. The flexible carbon chain and strong links helped the resin stay strong in the cold. This makes it good for aerospace and science.
Here is a table that compares some 3d printing methods and how they use resin:
| Technology | Cost Range | Precision Level | Material Types | Typical Applications |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| FDM | Low | Moderate | Thermoplastic filaments | Prototyping, hobby projects |
| SLA | Moderate | Very High | Photopolymer resins | Jewelry, dental, intricate designs |
| SLS | High | High | Nylon, composites | Functional parts, batch production |
| MJF | Moderate to High | High | Nylon, glass-filled powders | Functional prototypes, small-batch runs |
| DLP | Moderate | Very High | Photopolymer resins | Small, detailed parts |
Some common sla resin types are 355nm castable resin, 355nm high temperature resin, 355nm standard resin, and 355nm transparent resin. DLP printers use 405 high clear resin, 405 photopolymer resin, and 405 tough resin. These choices help people pick the right resin for their 3d print.
Popular brands for 3d printing resin are Siraya Tech, Phrozen, and Elegoo. Resin prices go from $16 to over $110 per kilogram. Sla resins usually cost $50 to $150 per liter. The price depends on the resin type and its features. Some resins are for beginners. Others are for experts or industry use.
How Resin 3D Printing Works

Printing Process
Resin printing uses a special workflow to turn liquid resin into solid 3D objects. The printer starts with a vat filled with resin. It lowers a build platform into the resin. A light source shines ultraviolet light onto the resin. This light triggers a chemical reaction called curing. The resin hardens only where the light touches it. The printer repeats this process layer by layer. Each layer sticks to the one below it. This method builds the 3D shape from the bottom up.
- Vat photopolymerization methods like SLA use a laser with a wavelength between 380 and 420 nanometers and less than 250 milliwatts of power. The laser scans across the x-y plane and cures a thin layer of resin, usually 25 to 100 micrometers thick. After each layer, the platform moves up or down to make space for the next layer.
- The curing process starts when the laser light hits the resin. Type I photoinitiators in the resin absorb the light and create free radicals. These free radicals start a chain reaction that turns the liquid resin into a solid.
- Printing settings such as layer height, orientation, and exposure time affect the strength and look of the finished part. For example, vertical layers often have higher tensile strength because of how the layers stack.
- The speed and power of the laser change between the edges and the inside of each layer. This affects how much the resin cures and can make the part stronger or weaker in different directions.
- UV spectroscopy at 420 nanometers helps measure how well the resin cures. It checks the absorption of light, which changes as the resin hardens.
- Post-processing steps like washing and extra curing improve the strength and finish of the part. Longer post-curing times and higher temperatures usually make the part stronger.
- The transparency of the resin affects how well the light passes through and how evenly the resin cures.
Note: The layer-by-layer curing process and post-processing steps are very important. They decide how strong and smooth the final 3D printed part will be.
Technologies (SLA, DLP, LCD)
Resin 3D printing uses three main technologies: SLA, DLP, and LCD. Each technology uses a different way to cure the resin and build the 3D object.
| Feature | SLA (Stereolithography) | DLP (Digital Light Processing) | LCD (Liquid Crystal Display) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Light Source | UV Laser | Digital Micromirror Device (DMD) | UV LED + LCD Masking |
| Curing Method | Point-by-point laser scanning | Full-layer projection | Full-layer exposure via LCD |
| Printing Speed | Slow (due to scanning each point) | Fast (cures entire layer at once) | Moderate to fast (full layer, limited by LCD) |
| Print Accuracy | High (finest detail, laser spot size) | High (limited by projector resolution) | Medium to high (depends on LCD pixel density) |
SLA uses a fine laser to cure the resin point by point. This gives the highest detail and smoothest surfaces. DLP uses a projector to cure an entire layer at once. This makes DLP faster than SLA, but the detail depends on the projector’s resolution. LCD printers use a UV LED light that shines through an LCD screen. The screen masks the light to cure each layer. LCD printing is usually faster than SLA and can be almost as fast as DLP. The detail depends on the pixel size of the LCD screen.
Surface roughness tests show that SLA makes the smoothest parts. DLP parts have a little more texture, but still look good. LCD parts can show tiny pixels, so the surface may not be as smooth. SLA is the slowest because it scans each point. DLP is the fastest because it cures a whole layer at once. LCD is in the middle, but new screens keep getting better.
After the printer finishes, the part needs post-processing. The user must wash the part in alcohol to remove extra resin. Then, the part goes into a UV curing chamber for extra curing. This extra step makes the part stronger and more stable. Post-processing is a key part of the resin workflow.
Resin 3D printing gives users a way to make detailed 3D objects with smooth surfaces. The curing process, the choice of technology, and careful post-processing all play a big role in the final result.
Resin 3D Printing Pros and Cons
Advantages
Resin printing is great for making models with lots of detail. Many people pick resin printing for smooth surfaces and sharp edges. The process uses UV curing and photopolymerization to harden each layer. This helps make prints with tiny features and a nice finish.
- Resin printing gives smoother surfaces than filament printing.
- It can show very small details, so it works well for tiny or tricky models.
- Some special resins, like those for dental work, are very accurate.
- Printing with resin is often faster than other 3D printing ways.
- After printing, sanding and extra curing make parts stronger and look better.
If you set up the printer right, you get good results every time. Many jobs use resin printing for test models, jewelry, and dental parts because it is so exact.
Tip: To get the best prints, always set up your printer and finish your parts the right way.
Disadvantages
Resin printing has some problems too. Resin and the printers cost more than filament ones. You must be careful with resin because it is unsafe before it hardens. Safety is very important when using resin printers.
- You need gloves, ppe, and eye protection when using resin.
- You must have good airflow so you do not breathe in fumes.
- Every print needs washing and more curing after printing.
- Resin can hurt your skin and eyes if you touch it.
- Resin and cleaning supplies can get expensive over time.
Safety rules help stop accidents. Always wear ppe and follow safety steps. Some people think the extra work and cost are hard. But people who want high detail and quality usually think it is worth it.
Resin Printer vs. Filament Printer
Print Quality
A resin printer uses sla to make objects with lots of detail. It cures liquid resin one layer at a time. This makes models smooth and gives sharp edges. Resin printers can show tiny details that filament printers miss. They work best for small 3d models, jewelry, and dental parts. Filament printers melt plastic to build shapes. These printers often leave lines you can see. Filament prints are good for bigger things but not for fine detail. The table below shows the main differences:
| Feature | Resin Printer (SLA) | Filament Printer (FDM) |
|---|---|---|
| Detail Level | Very High | Moderate |
| Surface Finish | Smooth | Layered |
| Small Features | Excellent | Limited |
Cost Comparison
Resin printers usually cost more than filament printers. Some resin printers start at $150, but many cost more. Resin for sla printers costs $16 to $110 per kilogram. Filament for FDM printers is usually cheaper. You also need gloves, cleaning alcohol, and a UV curing station for resin printers. These extras raise the total price. Over time, resin and cleaning supplies add up. Filament printers cost less to run, so they are better for people who print a lot or make big things.
Note: Think about both the printer price and the cost of materials when picking between sla and filament printers.
Ease of Use
Resin printers need careful setup and safety steps. Users must wear gloves and work where air moves well. The sla process needs washing and curing each print. This takes more time and effort. Filament printers are easier for beginners. They need less cleaning and have fewer safety rules. Resin printers need more care because resin is sticky and messy. Learning sla printing is harder, but you get better quality.
3D Printing Resin Applications
Common Uses
People use 3D printing resin for many kinds of projects. This material makes objects with smooth surfaces and fine details. Here are some ways people use it:
- Prototyping: Designers and engineers make test models with resin. These models help them see if shapes and sizes are right before making the real thing.
- Miniatures: Hobbyists and artists print miniatures for games or collections. Resin shows tiny details that other materials might not show.
- Dental Models: Dentists print teeth, crowns, and aligners with resin. These models help plan and fit dental work.
- Jewelry: Jewelers print rings, pendants, and small items. Resin printing makes sharp edges and smooth curves.
- Engineering Parts: Engineers use resin to make strong, detailed parts for machines or tools.
Tip: People pick different resins for each project. Some resins are tough. Others are flexible or can handle heat.
Industry Examples
Many industries use 3D printing resin for special jobs. Each industry picks a certain resin for its needs. The table below gives some examples:
| Industry | Application | Resin Type Used |
|---|---|---|
| Dental | Crowns, bridges, models | Biocompatible resin |
| Jewelry | Casting patterns, models | Castable resin |
| Engineering | Prototypes, gears | Tough or high-temp resin |
| Entertainment | Miniatures, props | Standard or flexible |
| Medical | Hearing aids, devices | Medical-grade resin |
Some companies mix resins to get special features. For example, they might mix tough resin with flexible resin. This makes a part that bends but does not break. Mixing resins helps make parts for special jobs.
3D printing resin makes models that look smooth and have lots of detail. But it costs more and you must be careful when using it. The table below shows how resin and filament printing are different:
| Aspect | Resin Printing | Filament Printing |
|---|---|---|
| Detail | Very high | Moderate |
| Surface Quality | Smooth | Layered |
| Cost | Higher | Lower |
| Safety | Needs careful handling | Fewer concerns |
If you want your first resin printer, think about safety rules and how much it will cost over time. Resin printers are best for people who want great detail and can follow all the safety steps.
FAQ
What is the shelf life of 3D printing resin?
Most 3D printing resins last about 12 to 18 months if stored in a cool, dark place. Users should check the bottle for the expiration date. Old resin may not cure well or could cause print failures.
What safety steps should users follow when handling resin?
Users should always wear gloves and safety glasses. Good airflow in the workspace helps reduce fumes. Skin contact with uncured resin can cause irritation. Users must wash hands after use and keep resin away from children and pets.
What happens if resin is not fully cured?
Uncured resin stays sticky and weak. Parts may break or lose detail. Users should always finish prints with extra UV light curing. This step makes the part strong and safe to handle.
What types of objects work best with resin printing?
Resin printing works best for small, detailed models. People use it for miniatures, dental models, jewelry, and prototypes. Large or simple shapes may not need resin’s high detail.
What should users do with leftover or waste resin?
Users must not pour resin down the drain. They should cure leftover resin with UV light until it hardens. After curing, users can throw it away with regular trash. Always follow local rules for safe disposal.